SOLUTIONS.
DIGITAL
Choose the perfect digital consulting plan for your business: Basic plan, intermediate plan and advanced plan. Each option offers customized solutions and effective digital marketing strategies to boost your online presence and increase your leads. Find out which one is best for you and start seeing amazing results today!
DIGITAL PARTNER
Minimum mandatory compliance period of 6 months*. Separate new website.
STARTER KIT
1.300€ /month
25 h / month
- Digital strategy: Definition of the marketing plan
- Paid Media: 2-channel management and strategy
- Social Networks: Strategy and management of 1 social network
- Content marketing: 2 posts per month
- Web maintenance and technical SEO: Basic
- Digital Analytics: Technical Implementation
- Dashboard: Definition of KPIs and measurement plan
- Email Marketing: 1 monthly mailing
- Dedicated Slack channel
- Monthly follow-up call
- Monthly Reporting
New website from: 2.500€.
GROWTH KIT
2.000€ /month
40 h / month
- Digital strategy: Definition of the marketing plan
- Video editing: 2 videos per month on stock or raw material provided by the client.
- Paid Media: Management and strategy of all channels
- Social Networks: Strategy and management of 3 social networks
- Content marketing: 2 posts per month
- Web Maintenance and Technical SEO: Advanced
- Digital Analytics: Technical Implementation
- Dashboard: Definition of KPIs and measurement plan
- Email Marketing: Automations and up to 3 monthly mailings
- Dedicated Slack channel
- Monthly follow-up call
- Monthly Reporting
New Web from: 1.700€.
ROCKET KIT
2.900€ /month
60 h / month
- Digital strategy: Definition of the marketing plan
- Video production and editing: 2 videos per month with the possibility of in house recording and generation of pieces for networks and paid
- Paid Media: Management and strategy of all channels
- Social Networks: Strategy and management of 4 social networks
- Design: Creation of creativities and ad hoc designs.
- Content marketing: 4 posts per month
- Web maintenance and technical SEO: Premium
- Digital Analytics: Technical Implementation
- Dashboard: Definition of KPIs and measurement plan
- Email Marketing: Automations and unlimited sendings
- Dedicated Slack channel
- Monthly follow-up call
- Monthly Reporting
New website from: 1.000€.
*The licenses of the digital tools established in the technology stack and the investment in Paid Media are not included in these fees and must be covered directly by the client.
On demand
Get a customized quote for your digital project.
Our team will make sure to offer you a tailor-made solution that fits your needs and budget.
Contact us to receive a free, no-obligation, personalized quote with a free audit!
Formation of companies
Each company is at a unique level of digital maturity. That’s why we offer a specific training plan for your company.
- Transformation: leadership and mindset change programs at the corporate level.
- Specialization: training in verticals such as growth marketing, big data and artificial intelligence, coding or Salesforce.
- Data: programs for data management or data analysts.
- New Talent: training designed to attract and train the best digital talent.
- Innovation: programs on agile methodologies, incubation and acceleration of startups
100% practical workshops in which the teams face first-hand the use of tools, platforms and problems that must be solved with solvency and skill, applying the knowledge acquired.
DIGITAL PARTNER
Looking to improve your online visibility, increase your customer base or boost your sales? Each of our plans is designed to offer you customized solutions and innovative and effective digital marketing strategies.
All plans include:
- Slack channel with direct communication
- Monthly follow-up call
- Definition of the marketing plan and digital strategy
- Management and strategy of means of payment
- SEO and content marketing
- Social media strategy
- Email marketing and marketing automation
- Account Based Marketing and Social Selling
- KPI definition and measurement plan
- Monthly reporting call
- Video editing and production
- Video podcast studio in Barcelona
- And much more…
On Demand
Get a customized quote for your digital project.
Our team will make sure to offer you a tailor-made solution that fits your needs and budget.
Contact us to receive a free, no-obligation, personalized quote with a free audit!
Training for companies
Each company is at a unique level of digital maturity. That’s why we offer a specific training plan for your company.
- Transformation: leadership and mindset change programs at the corporate level.
- Specialization: training in verticals such as growth marketing, big data and artificial intelligence, coding or Salesforce.
- Data: programs for data management or data analysts.
- New Talent: training designed to attract and train the best digital talent.
- Innovation: programs on agile methodologies, incubation and acceleration of startups
100% practical workshops in which the teams face first-hand the use of tools, platforms and problems that must be solved with solvency and skill, applying the knowledge acquired.
Get a customized quote for your digital project.
Our team of experts will make sure to offer you a tailor-made solution that fits your needs and budget.
Contact us to receive a free, no-obligation, personalized quote with a free audit!
Each company is at a unique level of digital transformation. That’s why we work on a specific training plan for your company within these five program categories:
- Transformation: leadership and mindset change programs at the corporate level.
- Specialization: training in verticals such as growth marketing, big data and artificial intelligence, coding or Salesforce.
- Data: programs for data management or data analysts.
- New Talent: training designed to attract and train the best digital talent.
- Innovation: programs on agile methodologies, incubation and acceleration of startups
100% practical workshops in which the teams face first-hand the use of tools, platforms and problems that must be solved with solvency and skill, applying the knowledge acquired.



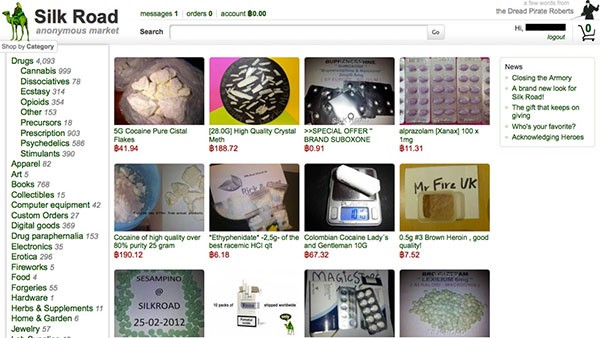
 Darknet websites can only be accessed in an encrypted form, so search engines like Google or Bing cannot find them. This means that users have to know where they want to access or know the address of the .onion page. However, you can find some help on hidden wikis that group the available links. Users can start an entire journey of discovery and try to find the right page.
Darknet websites can only be accessed in an encrypted form, so search engines like Google or Bing cannot find them. This means that users have to know where they want to access or know the address of the .onion page. However, you can find some help on hidden wikis that group the available links. Users can start an entire journey of discovery and try to find the right page.